Sugar factory equipment manufacturing
In addition to the equipment for processing sugar cane, we also offer auxiliary equipment required for the operation of sugar factories under the name Sugar factory equipment manufacturing.
- Home
- Fields-of-activity
- Sugar factory equipment manufacturing
Our fields of activity
- Fertilizer (Dap)
- Sulfuric acid
- Phosphoric acid
- Ammonia plant
- Cement factory
- Sugar factory
- Feed factory
- Power plant
- Hydroelectric plant
- Process equipment
- Chemical factory
- Pharmaceutical factory
- Oil factory
- Industrial facility construction
- Structural steel fabrication
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Propane Dehydrogenation
- Equipment design
Promotional brochure
Download our catalogue to see specific data about the service we provide and how we work.
Stay in touch!
Please feel free to contact us. We will get back to you within 1-2 business days. Or call us now.
Reliable sugar processing equipment
Equipment Manufacturing provides high-value engineering support to customers to manufacture custom sugar mill equipment or to enhance existing equipment and components. Whether you are building a new plant or optimizing your current operations, we help our customers maintain reliability and increase production by supplying readily available spare parts at competitive prices. From custom parts to maintenance and repairs, our engineers are ready to meet your equipment needs. Our equipment manufacturing product range has expanded to include a variety of solid and derivative pump solutions for our sugar customers.
Stages of sugar production
Sugar beets are harvested by digging them up from the ground in the fall and early winter. They are usually transported to the factory in large trucks because the transport distances are greater than in the cane industry. This is a direct result of sugar beets being a rotation crop that requires about 4 times the land area of an equivalent cane crop grown in monoculture. Since sugar beets come from the ground, they are much dirtier than sugar cane and must be thoroughly washed and separated from remaining beet leaves, stones and other trash material before processing. Therefore, sugar beets are carefully washed and temporarily stored in a beet bunker before being processed.
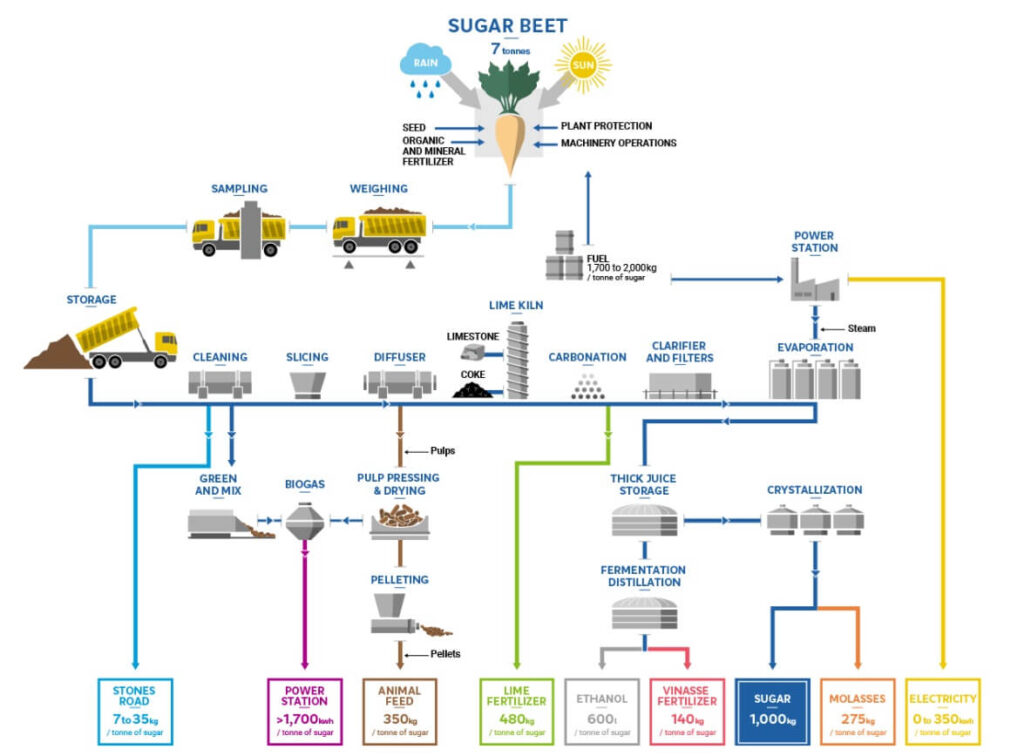
1. Slicing
Slicing machines cut beets into strips called cosettes, which have an average sugar content of between 16% and 20%.
2. Raw Juice Production
Sugar is extracted from the cosettes by means of hot water (around 70 °C) in a diffuser, where the cosettes move in the opposite direction of the water flow (counter-flow principle), in a process known as extraction. The resulting raw juice or liquor contains around 98% of the sugar in the sugar beet, as well as organic and inorganic components (so-called non-sugar) from the beet.
3. Purification of fruit juice
Non-sugar substances in raw juice are bound and extracted by means of lime (CaO) and carbonic acid gas (CO2), natural substances produced in the plant’s own lime kiln.
4.Filtering
Flocculated insoluble sugar-free substances and lime are filtered in filter units. The filtrate is known as fine juice and the filter residue is known as carbonating lime. It is an important soil improver and fertilizer spread on fields.
5. Intensive fruit juice production
To produce concentrated juice, thin juice is evaporated in a one-hour steaming process. The operation of on-site power plants provides a significant amount of energy required for sugar production. Steam generated in high-pressure boilers is used in turbogenerators to generate electricity. Waste steam from the turbines is used as process heat (cogeneration) to heat the evaporator station.
6.Crystalization
The concentrated juice is further thickened in boiling vessels under vacuum. The crystallization process is triggered by adding (adding) finely ground sugar to the concentrated juice. Further evaporation allows the crystals to reach the desired size.
7.Centrifugation
Sugar crystals are separated from the syrup by centrifugation. The separated syrup is subjected to two more crystallization processes.
8.Sugar
Pure, crystal clear sugar appears White when exposed to white light. White sugar contains at least 99.7% sucrose. The rest is actually moisture
9.Sugar drying
White sugar is dried in an air current, cooled and stored in silos. Packaged in many forms and in a large number of different household and industrial volumes, sugar is an important food and semi-luxury foodstuff that then reaches the end consumer.
10.Molasses
The syrup separated during the final crystallization step is known as molasses. Molasses contains the uncrystallized sugar from sugar beet (6-9%) as well as the soluble non-sugar substances from sugar beet. Molasses is a valuable ingredient for the baker’s yeast and animal feed industry, as well as for alcohol production.
11.Pellets
Pellets obtained from sugar water are mechanically pressed in the extraction tower and dried in the drying tunnel after molasses is added, then turned into pellets and sold as animal feed.