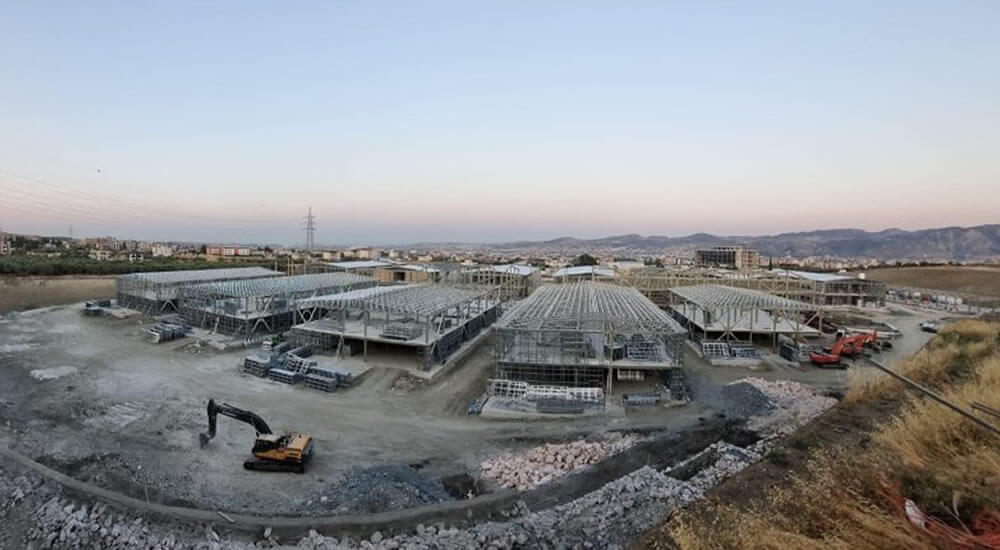
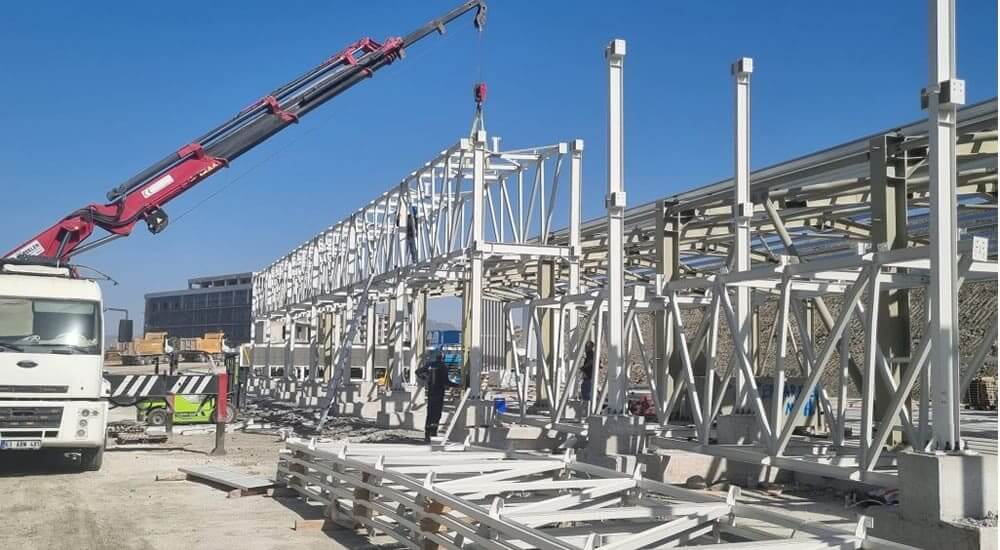
Structural steel fabrication
Structural steel fabrication is the process of bending, cutting and modeling steel to create a structure.
- Home
- Fields-of-activity
- Structural steel fabrication
Our fields of activity
- Fertilizer (Dap)
- Sulfuric acid
- Phosphoric acid
- Ammonia plant
- Cement factory
- Sugar factory
- Feed factory
- Power plant
- Hydroelectric plant
- Process equipment
- Chemical factory
- Pharmaceutical factory
- Oil factory
- Industrial facility construction
- Structural steel fabrication
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Propane Dehydrogenation
- Equipment design
Promotional brochure
Download our catalogue to see specific data about the service we provide and how we work.
Stay in touch!
Please feel free to contact us. We will get back to you within 1-2 business days. Or call us now.
Structural steel fabrication
For structural steel fabrication, steel parts are usually brought together to form different structures of predefined sizes and shapes. Fabrication steel is also known as carbon steel or unalloyed machine steel. These are unalloyed steels with a carbon content of approximately 0.20 to 0.60%.
They are also called carbon steels due to their high carbon content. While hardenability increases in direct proportion to the amount of carbon it contains, toughness is inversely proportional to the amount of carbon it contains. Low alloy steels are used if higher hardenability is desired. Fabrication steel is usually used in the engineering department for machine parts that do not require high strength.
Structural steel fabrication is the process of bending, cutting and modeling steel to form a structure. For structural steel fabrication, steel parts are usually brought together to form different structures of predefined sizes and shapes. It is a complex process that requires specialized knowledge, skills and resources to be successfully completed. You can rely on Arater structural steel fabrication experts for quality and fast solutions throughout this process.
What are the Advantages of Structural Steel Production?
✓ Steel is extremely durable, resistant to corrosion, and requires stretching. Steel has a higher strength than density, making it an excellent choice for construction and manufacturing.
✓ Structural steel is usually prefabricated and fabricated on site. Prefabrications help speed up projects by reducing the amount of work that needs to be done on site.
✓ Structural steel is cost-effective compared to other metals such as copper, silver, gold, aluminum, and magnesium. This low cost is very beneficial in construction and manufacturing.
✓ Structural steel components can be easily assembled after fabrication, increasing efficiency during assembly, saving significant cost and time.
✓ The metallurgical properties of steel allow it to be easily fabricated into any shape and size. Structural steel is manufactured by welding or bolting.
✓ The steel structure has a layer of flame retardant material, making it extremely resistant to fire. It is water resistant.
✓ Structural steel is an easily recyclable and environmentally friendly choice for metal fabricators. As YENA Engineering, we proudly work for an environmentally friendly and green future.
Structural Steel manufacturing stages
The structural manufacturing process consists of several stages. This process requires highly skilled and experienced technicians and engineers who can take raw components and turn them into quality products. With its experienced and talented staff in these processes, YENA Engineering provides superior benefits to structural steel needs. Each procedure is given below.
Stage 1
If you need to use steel parts, the idea stage plays an important role. Here, the processor can produce any structural steel product. To complete the processing of the steel, you need production drawings that correspond to the logistics of the project, such as delivery dates and budgets. The production of structural steel involves cutting, bending and welding the steel to create structures. Unlike different types of welding that repair or strengthen alloy steel, steel fabrication combines steel parts to create different structures. Usually the size and shape are predefined.
Stage 2
Cutting is the first part of structural steel manufacturing. High-quality steel can be used in laser cutters and water jets. It needs to be cut with various tools such as cutters and saws. This usually takes place in a closed production facility. Commonly used methods are saws (cold saws or band saws), flaring and sawing. Cutting is usually limited to a variety of structural steel parts. It is not used for larger components because the effort required and the resulting cut quality limit its economic and practical applicability. The trick comes later. Bending of structural alloys with special machines; there are still many manufacturers who prefer to hammer alloys by hand.
This also depends on the type of project. If you need to bend multiple steels repeatedly, it is much more convenient to use a machine. The third is welding. Once the steel parts are cut and shaped, the welding process begins to assemble them into a complete structure. It is used to create metal frames for buildings, bridges, vehicles and a variety of other complex structures. Structural welding is also used to cut and repair beams, supports and girders.
Stage 3
All steel parts are machined with part numbers and plate locations and are quickly, easily and accurately converted into fully assembled parts on site. The assembly of components is an integral part of the steel fabrication process. Once the components are assembled, they are checked to see if they meet specifications.
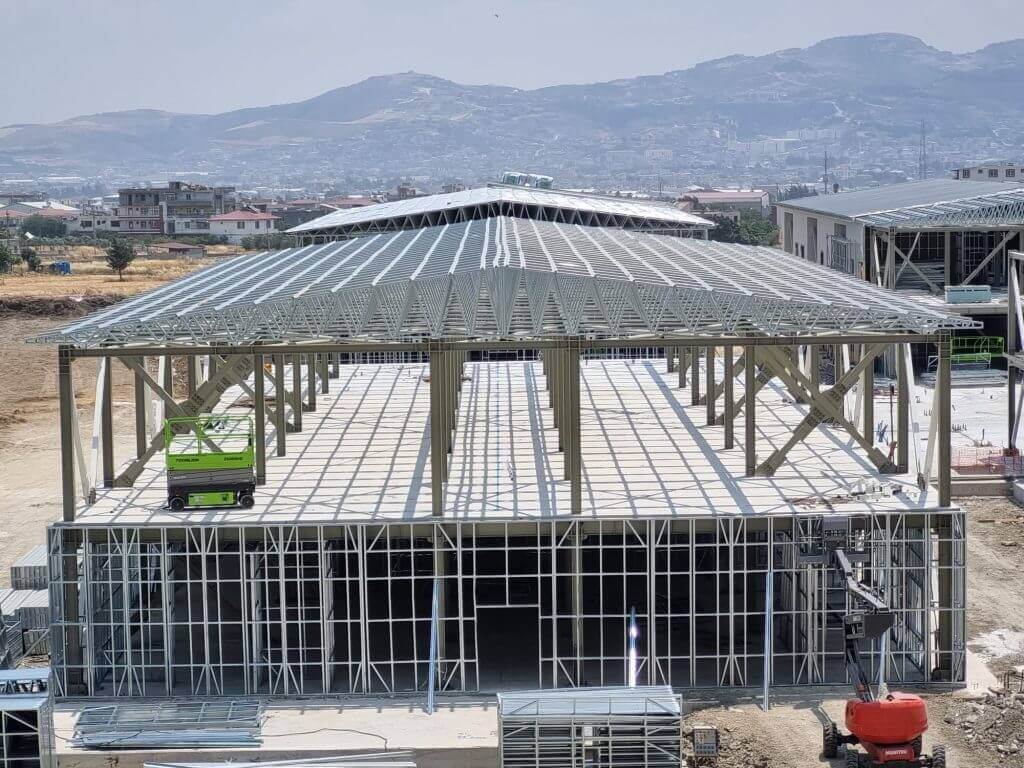

Use of Structural Steel in Construction
Production steel is also known as carbon steel or unalloyed machine steel. These are unalloyed steels with a carbon content of approximately 0.20% to 0.60%. They are also called carbon steels due to their high carbon content. Hardenability increases in direct proportion to the amount of carbon it contains, while toughness is inversely proportional to the amount of carbon it contains. If higher hardenability is desired, lower alloy steels are used. Production steel is generally used in the engineering department for machine parts that do not require high strength.
They are widely used in the automotive industry and machine manufacturing. The most commonly produced products are;
Gears
Bolts
Axles
Types of Structural Contradictions
SAE 1030, SAE 1040, SAE 1050, SAE 1060, ST50, ST52, ST60, ST70, C30, C40, C50, and C60. Structural steel grades are known as C30R, C40R, C50R, and C60R and are sulfur added steels. The sulfur addition is usually in the range of 0.020% – 0.035%.
Actual structural steel fabrication follows a process that uses advanced and powerful machinery to cut, bend, form, roll, drill, and weld steel components. Some of the tools used for this precision work are water jet cutters, precision laser torches, and plasma torches. Cutting the steel to the exact length is crucial to ensuring that the pieces fit together exactly.
After cutting and rolling, the steel is drilled or punched with precisely measured holes to allow components to be attached with bolts or rivets. Some steels are shaped using a press brake or bending roller machine. Certain components are welded together to increase overall strength and to bond the parts together. Throughout the entire fabrication process, blueprints and shop drawings will be followed to the exact specifications required.