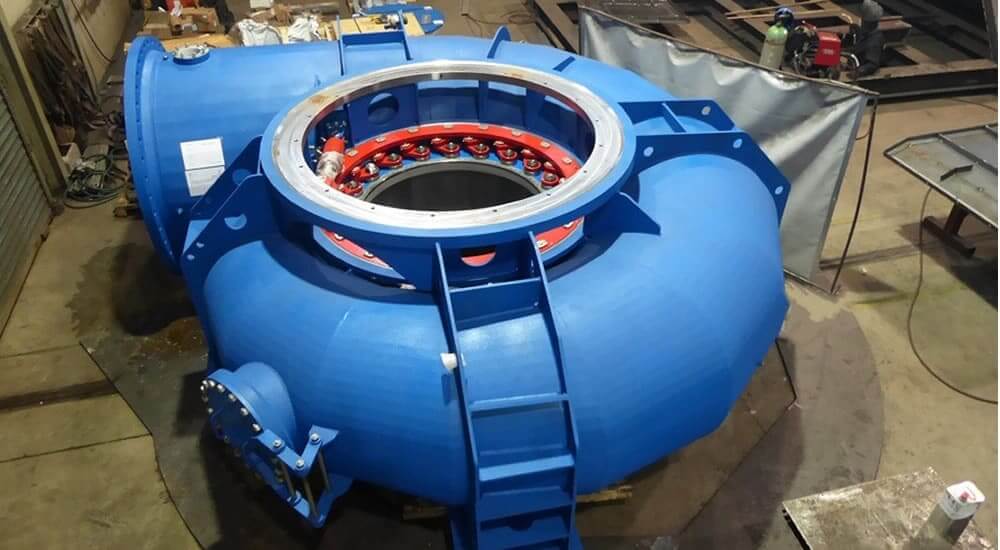
Hydroelectric power plant equipment manufacturing
Hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source derived from the movement of water. It is produced by large reservoirs or rivers that contain enough water to create a flow of water at a certain speed.
- Home
- Fields-of-activity
- Hydroelectric power plant equipment manufacturing
Our fields of activity
- Fertilizer (Dap)
- Sulfuric acid
- Phosphoric acid
- Ammonia plant
- Cement factory
- Sugar factory
- Feed factory
- Power plant
- Hydroelectric plant
- Process equipment
- Chemical factory
- Pharmaceutical factory
- Oil factory
- Industrial facility construction
- Structural steel fabrication
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Propane Dehydrogenation
- Equipment design
Promotional brochure
Download our catalogue to see specific data about the service we provide and how we work.
Stay in touch!
Please feel free to contact us. We will get back to you within 1-2 business days. Or call us now.
Hydroelectric power plant equipment manufacturing
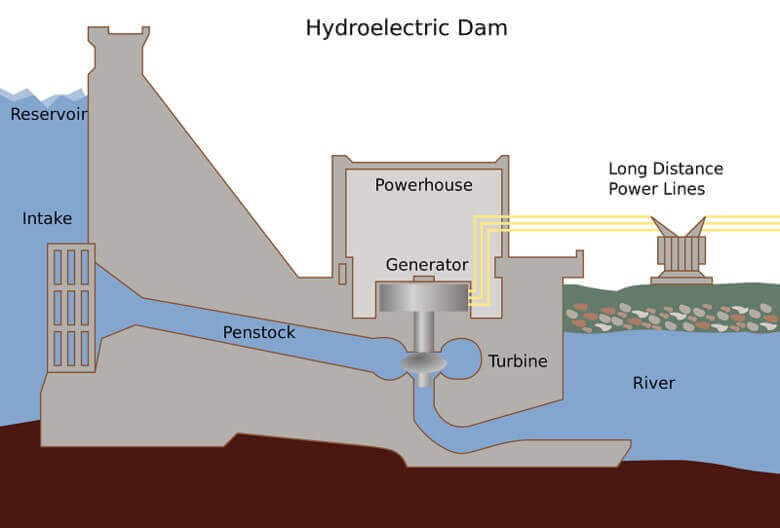
Hydroelectricity is produced by using falling water. For this purpose, a hydroelectric power plant needs a dam. This dam is placed on a water source, preferably a river. A dam is a huge wall that blocks the flow of the river, so a lot of water collects behind the dam. Near the bottom of the dam, there is an inlet through which the water is released into the dam. This inlet leads to a fall through the water channel inside the dam. The device used to extract energy from the falling water here is a turbine. Thermal power plants also use turbines, but there are some major differences between steam turbines and hydro turbines.
The turbine is connected to a generator by a shaft. When the water turns the turbine, electricity is produced. Hydroelectric power plants also have a pumped storage facility where water is kept as a reserve for periods of peak power demand. This is the hydroelectric equivalent of recharging a battery. When power demand is low, for example in the middle of the night, the dam uses a pump to pump the water back into the reservoir behind it. This water is then used during times of peak power demand.
Hydroelectricity refers to the production of electrical energy using hydroelectricity. Hydroelectricity here is essentially the gravitational force of falling water. This does not use water in the production of energy. In the previous article on thermal power plants, you learned that steam provides the motion in the turbines. Here, the high flow of water provides the rotation in the turbines, but we will get to that later. Coming back to hydroelectricity, it is the most widely used form of renewable energy, accounting for 3% of the world’s total energy consumption.
The cost of hydroelectricity is relatively low, which gives it a competitive advantage as an energy source. The average cost of electricity for a large hydroelectric power plant is very low. Since the energy production depends on the amount of water supplied, hydroelectric power plants have the advantage of being flexible. The output can be controlled according to the need.
What is a Hydroelectric Power Plant?
A hydroelectric power plant is an electrical generator that produces electricity from the flow of water. Hydroelectric engineering stands as one of the most effective renewable energy processes. It consists of two main components: a turbine and an electric motor. A turbine works to convert the kinetic energy of moving water into rotational motion, and an electric motor converts the rotational motion of the turbine into useful work.
Piping
How do hydroelectric power plants work?
A hydroelectric power plant consists of a set of facilities and electromechanical equipment used to convert the potential energy of water into electrical energy and can operate continuously. The available electrical energy is proportional to the flow rate and the drop in elevation. Hydroelectric power plants produce a renewable energy source that contributes to sustainability and the reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHG). In addition to reducing the negative effects of climate change, they are highly efficient and versatile, adapting to different scales of power generation from micro-generation to large-scale projects, providing clean electricity to entire regions. Hydroelectric power plants use a set of basic components and an ingenious process that efficiently exploits the hydrological cycle.
Industries use filters to remove unwanted substances from the main product during a process or application. Different types of filters are available in the market as per the requirements of the process such as air filter, hydraulic filter, panel filter, bag filter, screen filter, sand filter or gas filter. These perform the primary function of filtering or removing dust, purifying oil and fuel, removing debris and removing contaminants from a gas stream etc. Filters are generally used in the oil and gas industry.
They are available as a part of the entire pump package and make the disposal process easier, efficient and safer. One such example is brine disposal, which is of critical importance as gas and oil are harvested from porous rocks from which these fuels are extracted. Brine is a by-product and needs to be separated and further processed for proper disposal. Using conventional methods for filtration cannot facilitate cost-effective and efficient brine management, disposal and reuse. Therefore, filters are used to remove toxic oils and hydrocarbons from the product and ensure its safer discharge into the environment.
Catchment.
A strategic location is chosen in a river or reservoir where a large amount of moving water can be captured. This is done by means of a dam or weir that controls the flow of water.
Water transmission
The water is directed through a pipeline or transmission channel that directs the water to the hydroelectric power plant.
Turbine activation
Water reaches hydraulic turbines through pipelines that are activated by water flow.
Power generation
The turbines are connected to electrical generators called alternators, which produce electricity when water turns hydraulic turbines.
Current Transformation
The electricity produced in alternators is initially alternating current (AC). This usually has a low voltage, so a transformer is used to increase its voltage and make it suitable for long-distance transmission.
Transmission and distribution
The generated electricity is transmitted to the points where it is needed via high voltage transmission lines. Usually, an electrical substation is used to reduce the voltage before it is distributed to consumers.
Control and regulation
Hydroelectric power plants are equipped with control and regulation systems that monitor and adjust water flow and electricity production to maintain a continuous and stable energy supply.
Energy storage
Some hydroelectric power plants have the ability to store water in a reservoir. This makes it possible to regulate water flow and electricity production according to demand, making them a flexible energy source.