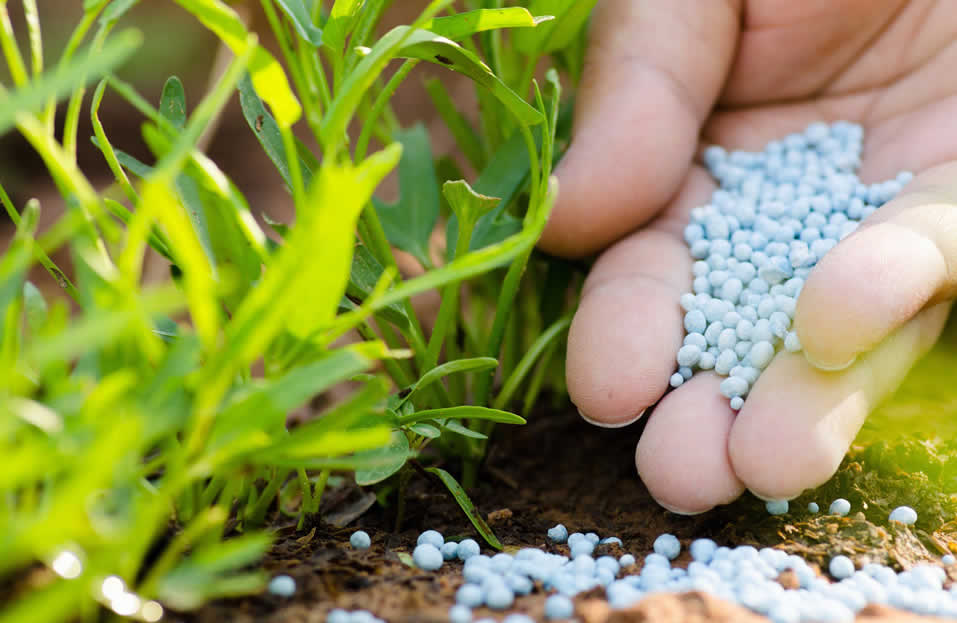
Fertilizer production
In the fertilizer production (DAP,NP,NPK) process, the basic reactions take place between ammonia and acids. In this process, liquid ammonia is used between +4 and +10 °C. In addition, phosphoric acid, which has a density of approximately 1.65 g/cm³ and contains 50-52% P2O5 and 4-5% H2SO4, is also added to the reaction.
Diammonium phosphate (DAP) fertilizer production is produced by reacting the DAP and monoammonium phosphate (MAP) mixture solution, which is formed by neutralizing liquid or gaseous ammonia with phosphoric acid in pipe or tank reactors, with liquid ammonia in the granulation drum. At the end of the production process, in order for the DAP fertilizer obtained to have the desired physical properties, drying, screening/crushing, cooling and coating processes are applied respectively and the final product is taken to stock storage.
In the granulation drum, not only the chemical reaction takes place, but also the granulation process is carried out. In order to ensure proper granulation in fertilizer production, the solid-liquid balance must be kept at a certain ratio. This ratio is approximately 4:1 for DAP fertilizer production; in other words, 4 tons of return product must be used to obtain 1 ton of final product.
You can contact us for our process engineering service regarding fertilizer production (DAP,NP,NPK,AS) and get information by calling 0533 573 80 70.

In the fertilizer production (DAP,NP,NPK) process, the basic reactions take place between ammonia and acids. In this process, liquid ammonia is used between +4 and +10 °C. In addition, phosphoric acid, which has a density of approximately 1.65 g/cm³ and contains 50-52% P2O5 and 4-5% H2SO4, is also added to the reaction.
Diammonium phosphate (DAP) fertilizer production is produced by reacting the DAP and monoammonium phosphate (MAP) mixture solution, which is formed by neutralizing liquid or gaseous ammonia with phosphoric acid in pipe or tank reactors, with liquid ammonia in the granulation drum. At the end of the production process, in order for the DAP fertilizer obtained to have the desired physical properties, drying, screening/crushing, cooling and coating processes are applied respectively and the final product is taken to stock storage.
In the granulation drum, not only the chemical reaction takes place, but also the granulation process is carried out. In order to ensure proper granulation in fertilizer production, the solid-liquid balance must be kept at a certain ratio. This ratio is approximately 4:1 for DAP fertilizer production; in other words, 4 tons of return product must be used to obtain 1 ton of final product.
Chemical Processes:
In the production of DAP Fertilizer production (Diammonium Phosphate), NP (Nitrogen Phosphate) and NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium) fertilizers, the basic chemical reactions take place between ammonia and various acids. These reactions are generally carried out in the temperature range of +4 to +10 °C. While liquid ammonia is included in this process, the phosphoric acid used in the reaction has a content of approximately 50-52% P₂O₅ and 4-5% H₂SO₄, and its density is stated as approximately 1.65 g/cm³. The relevant reactions can be summarized as follows.
Main Reaction;
NH3(liquid)+H3PO4 → NH4H2PO4+heat (formed in pipe reactor)
NH3(liquid)+NH4H2PO4 → (NH4)2HPO4+heat (formed in granulating drum bed)
With sulfuric acid:
a-1) NH3 (gas) +H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4+1800 kcal/kg NH3 gas (formed in washing systems)
a-2) NH3 (liquid) +H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4+1500 kcal/kg NH3 liquid (formed in pipe reactor)
With phosphoric acid
b-1) NH3(gas)+H3PO4→ NH4H2PO4+1500 kcal/kg NH3 gas (formed in washing systems (formed)
b-2) NH3(liquid)+H3PO4 → NH4H2PO4+1200 kcal/kg NH3 liquid (formed in pipe reactor)
b-3) NH3(gas)+NH4H2PO4 → (NH4)2HPO4+1300 kcal/kg NH3 gas (formed in washing systems)
b-4) NH3(liquid)+NH4H2PO4→(NH4)2HPO4+1000 kcal/kg NH3 liquid (formed in granulation drum)
You can contact us for our process engineering service regarding fertilizer production and get information by calling 0533 573 80 70.
Properties of fertilizers

CAN fertilizer production is used as a top fertilizer in all agricultural plants, especially wheat and barley, during the hoeing period and during irrigation. However, it is not suitable for rice farming. Since it has a neutral reaction, it can be used easily in all types of soil. CAN fertilizer should be applied in several stages, taking into account the nitrogenous fertilizer requirement of the plants, their growth phase and irrigation frequency.

Ammonium Nitrate fertilizer production can be used in the cultivation of all field crops and summer and winter vegetables except for rice farming. The amount to be applied per decare should be determined according to the results of soil analysis or in accordance with the advice of an expert. There are two different types of this fertilizer. The first type is applied directly to field crops as a top fertilizer from the soil. It is used by sprinkling in crops such as wheat and barley, and by mixing it into the soil with the help of a hoe in plants that require hoeing and irrigation before irrigation.

Urea is very useful in fertilizing almost all types of products to meet the nitrogen needs of plants. It offers the feature of being used at all stages of plant development. Urea fertilizer production can be applied as a base fertilizer (underground) during or before planting, and can also be preferred as a top fertilizer.

DAP fertilizer is widely used as a phosphorus-containing fertilizer production in our country as well as all over the world. Phosphorus is extremely important in plant nutrition, especially in the early development stages of the plant, as it supports root formation and plays a critical role in energy metabolism. This fertilizer, like other compound fertilizers, should be applied before planting or simultaneously with planting. In addition, it should be mixed into the appropriate depths of the soil to support the capillary root development of the plant. However, if it is applied after the seed germinates (from the emergence stage), its effect decreases significantly.

It is a fertilizer with 20% nitrogen (N) and 20% phosphorus (P2O5) as its active ingredient. It is ideal for fertilizing all plants grown in soils rich in potassium but deficient in nitrogen and phosphorus. It can be applied before sowing seeds, during sowing or before planting seedlings. As with other compound fertilizers, it is recommended to mix it into the soil 5-6 cm below the seed sowing depth.

It has been determined that zinc-added compound fertilizer increases yield in almost all products in zinc-poor soils. Zinc, which encourages root development in plants, increases the number of tillers and therefore the number of ears in plants such as wheat and barley, thus increasing both yield and quality. This fertilizer should be applied before or during seed sowing, and also before planting if seedlings are to be planted. As with all other compound fertilizers, it is recommended to mix it into the soil to reach a seed planting depth of 5-6 cm.

Ammonium Sulphate fertilizer, known as “sugar fertilizer” among farmers because its crystal structure resembles sugar, is widely used especially in plants with high sulfur needs. This fertilizer can be safely applied to products such as rice, onion, garlic, broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, canola, safflower, poppy, radish and carrot; and also to oil crops such as soy, peanut and sunflower before planting, during planting, during hoeing or before irrigation. However, its use is not recommended in acidic soils. In such a case, liming may be required to provide soil balance.

Among the base fertilizers, this fertilizer is the richest in terms of plant nutrients and can be used safely in all soils with high potassium content. Since nitrogen is in ammonium form, it is not washed deep into the soil due to excessive rainfall or irrigation and is not removed from the root area of the plant. It is an effective choice for increasing the yield and quality of plants such as cotton, corn, legumes (lentils, chickpeas, beans), onions and garlic. As with other base fertilizers, it is recommended to apply it under the soil before sowing seeds or seedlings in annual plants or simultaneously with sowing, i.e. 5-6 cm below the seed sowing depth.