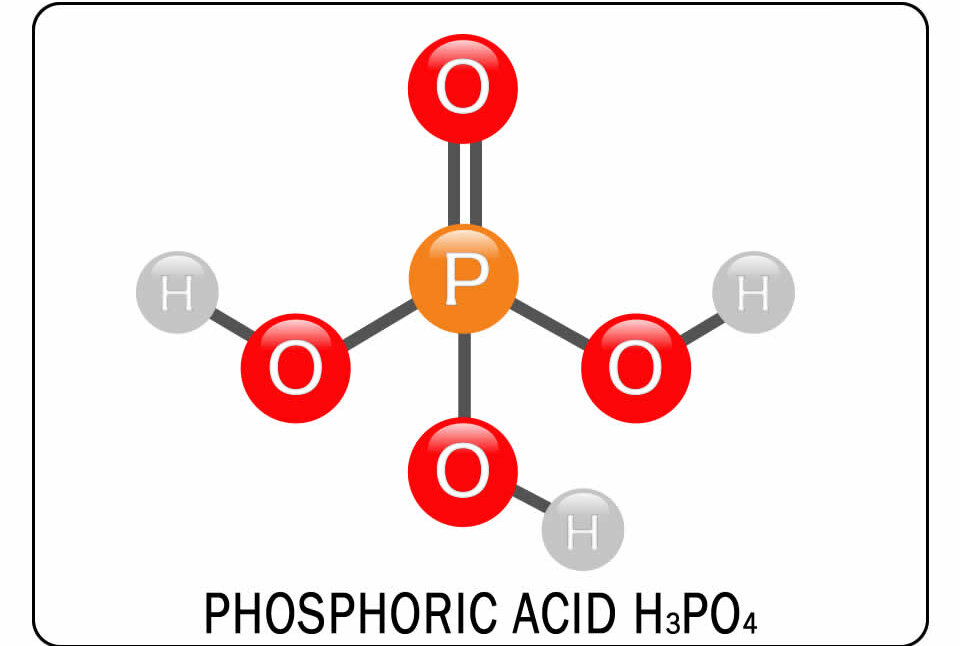
Phosphoric acid production
Phosphoric acid production Ca3 (PO4) 2 + 3H2SO4 + 6H2O → 2H3PO4 + 3 [CASO4 2H2O], according to the products formed as a result of the reaction, phosphate rock, sulfuric acid and water interaction with commercial quality phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and Jips as side products [CASO4 · 2H2O]. One of the most remarkable aspects of this process is the emergence of large amounts of gypsum.
For example, in some countries such as Japan, such facilities are used in gypsum production, and phosphoric acid is considered as by -product. Phosphoric acid production is usually performed by age method, which is mostly preferred in this process. Alternatively, hydrochloric (HCL) and nitric (HNO3) acids can also be used in the reaction. However, enterprises producing MCP (Mono Calcium phosphate) and DCP (DI Calcium phosphate), which are feed additives from phosphate rock, prefer hydrochloric acid.
You can contact us for our process engineering service regarding phosphoric acid production and get information by calling 0533 573 80 70.

Phosphoric acid physical properties
Pure phosphoric acid is a crystal form in the form of colorless, odorless, hygroscopic structure and does not flame. Commercial phosphoric acid is generally supplied as a juicy solution with a viscous structure containing 75-85 %phosphoric acid. It has been observed that the solution form solidifies at lower temperatures.
Melting point
– 42 ° C (pure)
– 21 ° C (85%concentration)
– 18 ° C (75%concentration)
Boiling point
– 260 ° C (pure)
– 154 ° C (85%concentration)
– 135 ° C (75%concentration)
Specific gravity
– 1,88 (pure)
– 1.69 (85%concentration)
– 1,58 (75%concentration)
Steam density
For pure phosphoric acid, this value is around 3.4.
Phosphoric acid chemical properties
It is a remarkable compound when we consider phosphoric acid production processes and chemical reactivity. It is obtained by two basic methods.In the first method, a direct reaction of phosphate rocks with sulfuric acid is performed and calcium sulfate (plaster) emerges as a by -product of the process. The second method is based on the burning of the elemental phosphorus and then the hydrate of oxidine.
Production of phosphoric acid is a corrosive acid with a capacity to form three different salt classes (primary, dibasic and tribazic phosphates) and show a high resolution in water. However, it does not react with strong costic substances, while it is abandoning metals such as iron and iron alloys. It also has the ability to produce flammable hydrogen gas when it comes into contact with metals.
Despite its chemical stability, phosphoric acid production can be decomposed by releasing poisonous gases when it reacts with organic substances such as alcohols, aldehydes, cyanide, ketones, phenols, esters, sulfitler, merchettanes or halogenic compounds. The production of toxic phosphorus oxide fumes during combustion is also a significant safety danger.
Considering these properties, careful controls and precautions are required for the production and use of Production of phosphoric acid