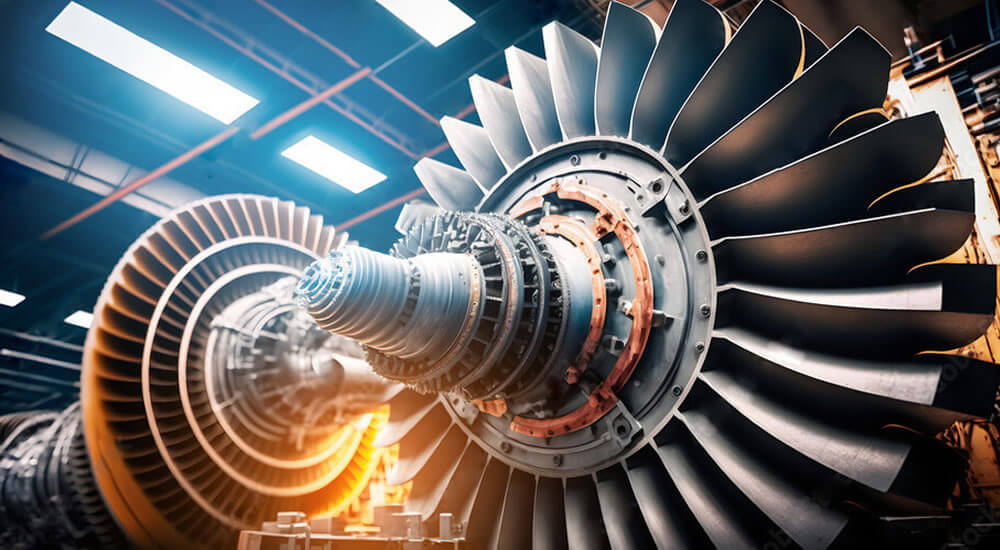
Power plant equipment manufacturing
Power plant equipment manufacturing produces equipment for the most common power plants in the world.
- Home
- Fields-of-activity
- Power plant equipment manufacturing
Our fields of activity
- Fertilizer (Dap)
- Sulfuric acid
- Phosphoric acid
- Ammonia plant
- Cement factory
- Sugar factory
- Feed factory
- Power plant
- Hydroelectric plant
- Process equipment
- Chemical factory
- Pharmaceutical factory
- Oil factory
- Industrial facility construction
- Structural steel fabrication
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Propane Dehydrogenation
- Equipment design
Promotional brochure
Download our catalogue to see specific data about the service we provide and how we work.
Stay in touch!
Please feel free to contact us. We will get back to you within 1-2 business days. Or call us now.
Power plant equipment manufacturing
The equipment used in thermal power plant manufacturing is part of a large-scale facility that converts heat energy into electricity. They are the backbone of global electricity generation, providing approximately 60% of the world’s electricity. However, their dependence on burning fossil fuels raises environmental concerns. The operating principle of thermal power plants involves using heat to generate high-pressure steam that drives turbines connected to generators. The steam is then condensed back into water and reused. Despite their reliability and efficiency, thermal power plants are a significant source of air pollution, emitting greenhouse gases such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and carbon dioxide.
How do power plants work?
As the world moves towards cleaner energy sources, power plants also need to adapt to reduce their environmental impact. This can be achieved by switching to cleaner fuels such as natural gas and implementing advanced pollution control technologies. Power plants play a crucial role in generating electricity, but they need to evolve to address their environmental impact.
Heat generation
Boiling Water
This intense heat is then used to boil water in a high-pressure vessel, creating high-pressure steam. Steam is like a powerful force waiting to be brought under control.
Steam Turbine
This intense heat is then used to boil water in a high-pressure vessel, creating high-pressure steam. Steam is like a powerful force waiting to be brought under control.
The high-pressure steam is directed into a steam turbine. It’s a bit like a giant fan that spins under the power of the steam. As the turbine spins, it drives an electric generator.
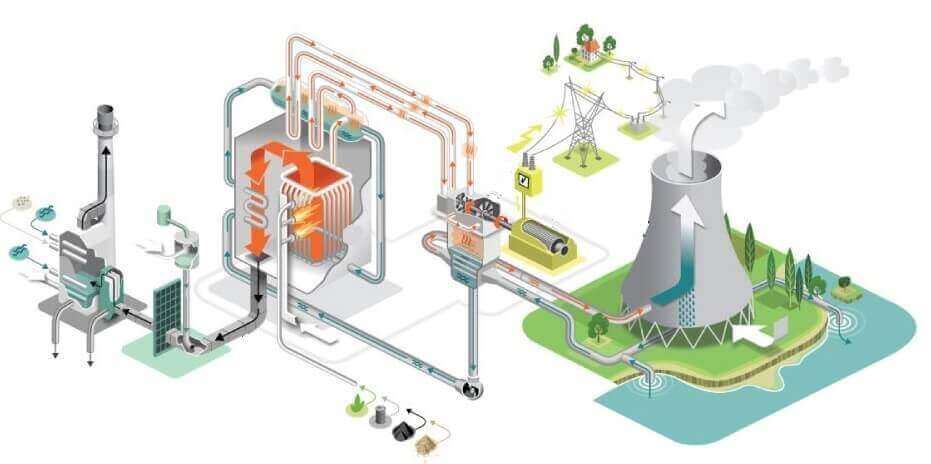
Generating Electricity
Recycling Heat
But the process doesn’t end there. After the steam has done its work, it leaves the turbine at a lower pressure. It is still hot, though. This hot steam is sent to the steam condenser.
Cooling and Recycling
In the condenser, the hot steam is cooled and converted back into water. This condensed water is then returned to the high-pressure vessel to start the cycle over again.
Power generation
Unblock your potential growth and unlock your full potential by empowering the future.
Maximize your efficiency by improving energy conversion and using high-quality equipment. These machines ensure precise turbine rotation, specific generator activity, efficient compression and engine performance, resulting in greater energy production, increased grid stability and reduced emissions. By ensuring optimal operating conditions, you can increase the efficiency of power generation facilities and provide reliable, sustainable electricity for society’s growing energy needs.
Production process
Every application in the power generation sector requires some type of industrial rotating equipment. The trouble-free operation and regular maintenance of these equipment are of great importance for the efficiency and safety of the sector.
Conventional Electricity Generation
In conventional power plants such as coal, natural gas and nuclear power plants, electricity is produced by large-scale rotating turbines.
Thermal Energy
Thermal energy obtained from fuel combustion or nuclear reactions is used to produce high-pressure steam that drives the turbines.
Hydroelectric Power Plants
In hydroelectric power plants, the kinetic energy of water contributes to the production of electricity by driving the turbines.
Wind Energy
Wind turbines function as rotating machines that convert the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy and then into electrical energy.
Compressors
In gas turbine power plants, rotary compressors are used to compress the air intake, thus effectively igniting the fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
Pumps
In power plants, different types of pumps are used for various functions such as circulation of cooling water, water supply to boilers, oil transportation between machines and fuel transfer.
Generators
Among the rotary machines, generators have become a basic component of almost all power generation systems by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers, although not rotary machines themselves, are usually used with rotary machines such as pumps or fans to increase heat transfer between fluids.
Maintenance and Safety Equipment
Various equipment such as circulation pumps, ventilation fans and rotary feeders used in fuel supply systems are used for maintenance and safety applications in power plants.
Waste Management
In the transportation and processing of waste materials, the use of rotary mechanisms such as pumps may often be required to transport waste materials to appropriate disposal points.